The benefits of Aloe Vera Leaf Gel
Aloe Vera Leaf Gel is found in the follow Dr. Hennen products:
General Benefits of Supplementing with Aloe Vera
Key Takeaway:
Oral aloe vera supplementation demonstrates blood glucose lowering, anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and oral health benefits in clinical studies, though evidence quality remains limited due to small sample sizes and variability in preparation methods. Safety concerns exist regarding whole leaf preparations containing anthraquinones.
1. Blood Glucose and Metabolic Effects
A systematic review of 10 controlled clinical trials found that oral administration of aloe vera might be a useful adjunct for lowering blood glucose in diabetic patients as well as reducing blood lipid levels in patients with hyperlipidemia. Specific studies reported reductions from 250 to 141 mg/dL in treatment groups with no change in controls. The mechanisms likely involve improved insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, though the active compounds responsible remain unclear.[1][2]
2. Oral Health and Dental Applications
2.1 Antimicrobial Activity
Aloe vera gel demonstrates significant antimicrobial effects against oral pathogens:
- Inhibits growth of Candida albicans, the most common candida species in the oral cavity[3]
- Shows activity against Streptococcus mutans, S. sanguis, S. viscosus, and C. albicans in dental products[3]
- Contains natural anthraquinones (aloe emodin, aloin, barbaloin) responsible for antimicrobial properties[3]
2.2 Periodontal Disease Treatment
Clinical trials show aloe vera’s effectiveness in treating gum disease:
- Significantly reduces gingival inflammation and bleeding compared to conventional treatments alone
- In combination with scaling and root planing, produces greater reductions in probing depth and gingival index at 30 and 60 days[4]
- Mouthrinses containing aloe vera show remarkable reduction in gingivitis and plaque accumulation[3]
2.3 Oral Ulcer Treatment
A systematic review and meta-analysis of 9 randomized controlled trials (847 participants) examining aloe vera for oral ulcers found:
- No significant differences in pain scores (VAS) compared to controls
- Significantly shorter therapy duration favoring control groups over aloe vera[5]
- Mixed evidence for ulcer size reduction and healing rates
3. Anti-inflammatory and Wound Healing Properties
Aloe vera contains over 75 active compounds including amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and polysaccharides that contribute to:
- Reduced inflammation through inhibition of pro-inflammatory pathways
- Enhanced wound healing via stimulation of fibroblast proliferation and collagen synthesis
- Tissue repair acceleration in oral mucosa and skin applications[3]
Conclusion:
Oral aloe vera supplementation offers modest but clinically meaningful benefits for blood glucose control, oral health maintenance, and inflammatory conditions. However, product quality and standardization are critical—decolorized preparations with low anthraquinone content provide the best safety-to-benefit ratio for long-term use.
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10885091/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK67693/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4253296/
- https://www.todaysrdh.com/ancient-cures-modern-times-surprising-benefits-aloe-vera-oral-health/
- https://pdfs.semanticscholar.org/a280/63f7772cd03a98735de3dcc70d0aab779f9a.pdf
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6349368/
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/supplement-guide-aloe-vera
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4439686/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/aloe-vera-for-gums
- https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT04734106
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK92765/
- https://www.premiersmilespa.com/blog/dental-care/can-aloe-vera-maintain-or-improve-my-oral-health
Specific Benefits of Oral Aloe Vera Supplements for Skin Care
Oral aloe vera supplementation offers scientifically-backed benefits for skin health through internal mechanisms that complement topical applications. Research demonstrates that consuming aloe vera can improve multiple aspects of skin appearance and function from within.
Key Active Compounds for Skin Health
Acemannan, the primary bioactive polysaccharide in aloe vera, serves as the cornerstone of oral supplementation benefits[1][2]. This β-(1,4)-linked acetylated mannose polysaccharide comprises the most therapeutically active component, working through multiple pathways to support skin health[1]. Additionally, aloe sterols—specifically lophenol and cycloartenol—contribute significantly to skin improvements when consumed orally[3][4].
Enhanced Collagen Production and Skin Structure
The most well-documented benefit of oral aloe vera is its ability to stimulate collagen synthesis. Multiple clinical trials have demonstrated that oral supplementation significantly increases type I procollagen production while decreasing matrix metalloproteinase-1 (MMP-1) expression, which breaks down existing collagen[5][3].
A landmark 2009 study involving 30 women over age 45 found that daily oral aloe vera gel supplementation at doses of 1,200-3,600 mg significantly improved facial wrinkles and elasticity after 90 days[5]. Both dosage groups showed measurable improvements in skin texture, with wrinkle depth decreasing significantly as measured by precision skin analysis equipment. The study revealed increased type I procollagen gene expression and substantially enhanced collagen protein presence throughout the dermis[5].
More recent research has confirmed these findings with lower doses. A 2020 clinical trial demonstrated that just 19 μg daily of aloe sterols (approximately half the previously tested amount) significantly increased collagen scores after 12 weeks, confirming that even minimal doses can provide meaningful skin benefits[3][6].
Improved Skin Barrier Function and Hydration
Oral aloe vera supplementation enhances the skin’s natural barrier function through multiple mechanisms. Research shows that regular consumption significantly reduces transepidermal water loss (TEWL) while increasing overall skin moisture content[3][6][7].
The 2020 study of 122 healthy volunteers found that low-dose aloe sterol supplementation not only improved collagen production but also significantly enhanced skin barrier function[3]. Participants showed measurable improvements in skin hydration, with those having initially dry skin experiencing the most pronounced benefits. The enhanced barrier function helps the skin retain moisture more effectively and provides better protection against environmental stressors[6].
Anti-Inflammatory and Healing Benefits
Acemannan’s powerful anti-inflammatory properties translate to visible skin improvements when consumed orally. The compound works by suppressing pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β while activating anti-inflammatory pathways[1][8]. This systemic anti-inflammatory effect helps reduce skin redness, irritation, and inflammatory conditions.
Clinical studies have documented significant improvements in objective skin conditions, including reduced facial erythema and decreased pruritis (itching) on both inner and outer arms after 12 weeks of oral aloe supplementation[3][9]. These improvements were not observed in placebo groups, confirming the specific benefits of aloe vera consumption.
Acne Management and Skin Clarity
Oral aloe vera supplementation offers unique benefits for acne-prone skin through multiple mechanisms. Acemannan activates macrophages and enhances immune cell function, helping the body naturally combat acne-causing bacteria like Propionibacterium acnes[1][10]. Additionally, the anti-inflammatory effects help reduce the inflammatory response that contributes to acne severity.
Research indicates that the folic acid, chromium, potassium, and other compounds in aloe vera are particularly beneficial for skin health when consumed internally[11]. Clinical trials have shown significant improvement in subjective visual analog scale ratings for skin acne after 12 weeks of oral supplementation[3].
Antioxidant Protection and Anti-Aging Effects
Aloe vera’s rich antioxidant profile—including vitamins A, C, and E—provides systemic protection against free radical damage when consumed orally[12][13]. This internal antioxidant support helps prevent premature aging caused by oxidative stress from environmental factors like pollution and UV radiation.
The vitamin C content specifically supports immune function and aids in the synthesis of hyaluronic acid, which is crucial for skin hydration and elasticity[14][15]. Regular consumption helps maintain skin strength and resilience from within, complementing external skincare efforts.
Clinical Evidence and Dosing
Multiple controlled clinical trials support the efficacy of oral aloe vera for skin health:
- Low-dose effectiveness: As little as 19 μg daily of aloe sterols shows measurable benefits[3][6]
- Standard dosing: Most studies use 300-600 mg of aloe vera gel powder daily[5]
- Timeline for results: Significant improvements typically appear after 8-12 weeks of consistent use[5][3]
- Safety profile: No significant adverse effects reported in clinical trials at recommended doses[5][3]
Mechanisms of Action
Oral aloe vera works through several pathways to benefit skin:
- Enhanced cellular communication: Acemannan supports cell-to-cell communication that influences physiological functions[16]
- Improved nutrient delivery: Polysaccharides enhance cellular nutrient and oxygen delivery while facilitating waste elimination[17]
- Systemic hydration: Internal consumption provides hydration that complements topical moisturizing[12][15]
- Immune modulation: Supports balanced immune responses that benefit skin health[8][18]
Optimal Usage Guidelines
For maximum skin benefits from oral aloe vera supplementation:
- Choose standardized products containing verified acemannan content (≥10% polysaccharides)[16]
- Maintain consistent daily intake for at least 12 weeks to see measurable results[3][6]
- Look for low-aloin products (<10 ppm) to avoid digestive irritation[16]
- Consider combination with topical aloe products for synergistic effects[19]
Oral aloe vera supplementation represents a scientifically-validated approach to supporting skin health from within. The combination of enhanced collagen production, improved barrier function, anti-inflammatory effects, and antioxidant protection provides comprehensive benefits that complement external skincare routines. While effects are modest compared to prescription treatments, the safety profile and multiple mechanisms of action make oral aloe vera a valuable addition to comprehensive skin health strategies.
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC11510295/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10283281/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7496846/
- https://karger.com/spp/article/29/6/309/295888/Effects-of-Aloe-Sterol-Supplementation-on-Skin
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC2883372/
- https://www.naturalhealthresearch.org/aloe-sterol-improves-skin-function-in-healthy-female-volunteers/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/1346-8138.15428
- https://e-fsbh.org/DOIx.php?id=10.52361%2Ffsbh.2023.3.e8
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/1346-8138.15428
- https://www.mdpi.com/2076-2607/12/10/2070
- https://www.blume.com/blogs/blume-university/benefits-of-hydrating-aloe-vera-juice-for-your-skin
- https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/aloe-vera-juice-benefits
- https://yemenjmed.com/admin/uploads/1/9_pdf.pdf
- https://www.today.com/health/diet-fitness/aloe-vera-juice-benefits-rcna202186
- https://www.prevention.com/food-nutrition/a64592429/aloe-vera-juice-benefits/
- https://us.mannatech.com/en-uk/products/acemannan/
- https://amb-wellness.com/acemannan/
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4440021/
- https://wellbeingnutrition.com/blogs/skin/using-aloe-vera-for-improving-skin-health
Specific Benefits of Oral Aloe Vera Supplements for General Colon Health
Oral aloe vera supplementation offers significant benefits for general colon health through multiple scientifically-documented mechanisms. The primary bioactive compound, acemannan—a β-(1,4)-linked acetylated mannose polysaccharide—drives most of these therapeutic effects when consumed regularly.
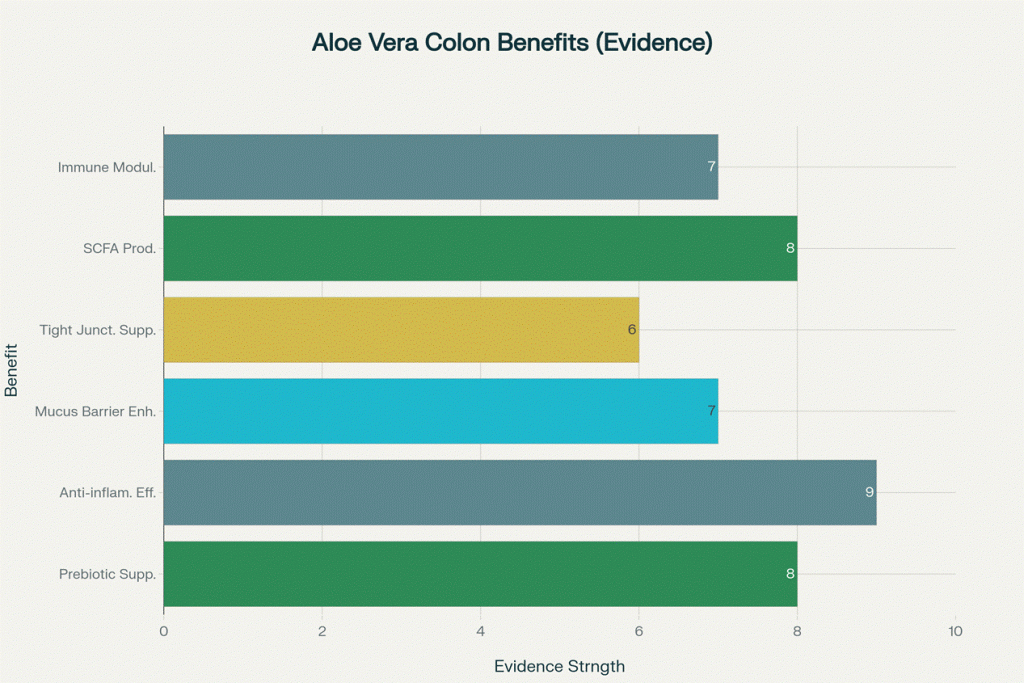
Key Colon Health Benefits of Oral Aloe Vera Supplementation (Evidence Strength Scale 1-10)
Prebiotic Effects and Microbiome Support
Acemannan acts as a powerful prebiotic, selectively nourishing beneficial gut bacteria and promoting a healthy colonic microbiome. Research demonstrates that aloe vera polysaccharides stimulate the growth of beneficial bacteria, particularly Bifidobacterium species, with fructans from aloe vera inducing a 13.73% increase in Bifidobacterium populations[1]. The prebiotic effects are comparable to or exceed those of commercial prebiotics like fructooligosaccharides (FOS)[1].
Acemannan’s unique β-(1,4) glycosidic bonds cannot be digested by human enzymes but are readily cleaved by beneficial colonic bacteria[2]. This selective fermentation process allows acemannan to reach the colon intact, where it serves as a preferred fuel source for health-promoting microorganisms[3].
Short-Chain Fatty Acid (SCFA) Production
Oral aloe vera significantly enhances the production of beneficial short-chain fatty acids in the colon. When acemannan is fermented by colonic bacteria, it produces substantial amounts of acetate, propionate, and butyrate—the three primary SCFAs that support colon health[4][5].
Butyrate production is particularly notable, as this SCFA serves as the primary energy source for colonocytes (colon cells) and has anti-inflammatory properties[2]. Studies show that fructans from aloe vera produce greater amounts of total SCFAs compared to commercial prebiotics, with butyrate constituting 23% of total fatty acids produced from aloe fructans[1]. Acemannan specifically increases acetate concentrations significantly, providing additional metabolic benefits[1].
Anti-Inflammatory Protection
Acemannan provides potent anti-inflammatory effects that protect the colon from chronic inflammation—a key factor in maintaining long-term colon health. Clinical studies demonstrate that oral aloe vera significantly reduces pro-inflammatory cytokines including IL-6, IL-1β, and TNF-α[6][7] while simultaneously increasing anti-inflammatory IL-10 levels[6].
The anti-inflammatory mechanisms work through multiple pathways: acemannan suppresses NF-κB activation, a key inflammatory signaling pathway, and reduces the production of inflammatory mediators like prostaglandins and leukotrienes[8]. These effects help maintain the delicate balance between immune protection and tissue preservation in the colon.
Enhanced Mucus Barrier Function
Oral aloe vera supplementation strengthens the protective mucus layer that lines the colon, serving as the first line of defense against harmful substances and pathogens. Animal studies show that aloe vera treatment significantly upregulates mucin proteins MUC2 and MUC5AC and increases the thickness of the mucus layer in the colon[6].
The enhanced mucus production occurs through upregulation of p-PKC and p-ERK expression[6], pathways that control mucin synthesis and secretion. This protective mucus barrier improvement helps prevent the direct contact of irritating substances with the colonic epithelium, reducing inflammation and supporting overall colon health[8].
Intestinal Barrier and Tight Junction Support
Acemannan helps maintain and repair the intestinal barrier function, which is crucial for preventing “leaky gut” and maintaining colon health. Research demonstrates that processed aloe vera gel enhances the expression of zonula occludens (ZO)-1, a critical tight junction protein[9][10].
The mechanism involves activation of the MAPK/ERK signaling pathway, which inhibits the translation repressor 4E-BP1, ultimately leading to increased production of tight junction proteins[9]. Clinical studies show that oral aloe vera treatment reduces urinary lactulose/mannitol ratios, indicating improved intestinal barrier function[9].
Immune System Modulation
Acemannan provides balanced immune support in the colon through activation of innate immune cells and modulation of inflammatory responses. The polysaccharide activates macrophages and dendritic cells while promoting a shift toward anti-inflammatory immune responses[11][12].
Studies show acemannan increases regulatory T cells and promotes the production of anti-inflammatory cytokines, helping maintain immune homeostasis in the colon[12]. This balanced immune modulation protects against both infections and excessive inflammatory responses that can damage colon tissue.
Protection Against Oxidative Stress
Oral aloe vera provides antioxidant protection for colon tissues through multiple mechanisms. The supplement increases endogenous antioxidant enzymes including superoxide dismutase (SOD) and catalase[13], which neutralize harmful free radicals that can damage colon cells.
Acemannan’s antioxidant effects extend beyond direct scavenging to include regeneration of other important antioxidants like glutathione, vitamin C, and vitamin E[5]. This comprehensive antioxidant support helps protect against oxidative damage that contributes to colon inflammation and cellular dysfunction.
Clinical Evidence and Safety
Human clinical trials support the safety and efficacy of oral aloe vera for colon health. A randomized controlled trial found that oral aloe vera gel (100 mL twice daily for 4 weeks) produced clinical improvements in inflammatory bowel conditions, with no significant adverse events reported[14].
The therapeutic effects appear within 4-8 weeks of consistent supplementation, with benefits including reduced inflammation, improved symptoms, and enhanced tissue healing[14][7]. Long-term safety studies indicate that properly processed aloe vera gel (free from anthraquinones) is well-tolerated for extended use[11].
Optimal Dosing and Preparation
For general colon health support, research supports doses of 300-600 mg daily of standardized aloe vera gel powder or equivalent liquid preparations[15][14]. Products should contain ≥10% polysaccharides and <10 ppm aloin to ensure safety and efficacy[16].
Acemannan content is crucial for therapeutic benefits, with effective products typically containing at least 150 kDa molecular weight fractions that resist digestion and reach the colon intact[15]. Consistency is key—benefits become apparent after 8-12 weeks of regular supplementation[9].
The evidence strongly supports oral aloe vera supplementation as a comprehensive approach to maintaining colon health through multiple complementary mechanisms. The combination of prebiotic effects, anti-inflammatory action, barrier support, and immune modulation makes acemannan-rich aloe vera a valuable tool for supporting long-term colon wellness and function.
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6175553/
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/drugs-supplements-aloe/art-20362267
- https://aloevonderweid.com/en/news-blog-en/acemannan-a-natural-gastroprotectant/
- https://www.goodrx.com/well-being/diet-nutrition/benefits-of-aloe-vera-juice
- https://www.verywellhealth.com/aloe-vera-as-a-complementary-treatment-for-ibd-1942472
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34427371/
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/320532
- https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.jafc.7b04100
- https://www.healthline.com/health/ulcerative-colitis/aloe-vera-for-ulcerative-colitis
- https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC10385217/
- https://www.healthline.com/health/food-nutrition/aloe-vera-juice-benefits%23side-effects
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0147651324014271
- https://www.hollandandbarrett.com/the-health-hub/conditions/digestive-health/is-aloe-vera-good-for-your-bowels/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0144861722003691
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/supplement-guide-aloe-vera
- https://caringsunshine.com/relationships/relationship-intestinal-system-and-acemannan/


